Display raw and compressed images, as well as compressed videos, with 2D annotations like text labels, circles, and points. Superimpose 3D markers for additional context.
Supported encodings
| Raw images | Compressed images | Compressed videos |
|---|---|---|
8UC1 | webp | h264 |
8UC3 | jpeg | |
16UC1 | jpg | |
32FC1 | png | |
bayer_bggr8 | ||
bayer_gbrg8 | ||
bayer_grbg8 | ||
bayer_rggb8 | ||
bgr8 | ||
bgra8 | ||
mono8 | ||
mono16 | ||
rgb8 | ||
rgba8 | ||
uyvy or yuv422 | ||
yuyv or yuv422_yuy2 |
Supported messages
To use this panel, your data source must provide messages conforming to 3D marker message types or one of the following supported schemas.
RawImage
| framework | schema |
|---|---|
| ROS 1 | sensor_msgs/Image |
| ROS 2 | sensor_msgs/msg/Image |
| Custom | foxglove.RawImage |
CompressedImage
| framework | schema |
|---|---|
| ROS 1 | sensor_msgs/CompressedImage |
| ROS 2 | sensor_msgs/msg/CompressedImage |
| Custom | foxglove.CompressedImage |
CompressedVideo
Record H.264 data using the Annex B format, avoiding B frames.
| framework | schema |
|---|---|
| Custom | foxglove.CompressedVideo |
CameraCalibration
Provide optional camera calibration data to render 3D entities in the Image panel, or render images in the 3D panel. Calibration data is not required to display ImageAnnotations since they use pixel coordinates.
Foxglove supports distortion models plumb_bob and rational_polynomial.
| framework | schema |
|---|---|
| ROS 1 | sensor_msgs/CameraInfo |
| ROS 2 | sensor_msgs/msg/CameraInfo |
| Custom | foxglove.CameraCalibration |
ImageAnnotation
| framework | schema |
|---|---|
| ROS 1 | visualization_msgs/ImageMarker |
| ROS 2 | visualization_msgs/msg/ImageMarker |
ImageAnnotations
| framework | schema |
|---|---|
| ROS 1 | foxglove_msgs/ImageMarkerArray |
| Custom | foxglove.ImageAnnotations |
Settings
General
| field | description |
|---|---|
| Topic | Camera image or video topic to display |
| Calibration | Calibration topic to use for distortion and 3D markers |
| Sync annotations | Display images and 2D annotations only when their messages' timestamps match. Newly received 2D annotation messages will be buffered until a matching set can be displayed. Not yet supported for CompressedVideo topics. |
| Flip horizontal | Flip image horizontally over a vertical axis |
| Flip vertical | Flip image vertically over a horizontal axis |
| Rotation | Rotate image by 90°, 180°, or 270° |
| Color mode |
|
| Color map | Only shown if "Color mode" is set to "Color map". For mapping mono16 and 16UC1 image values to colors:
|
| Gradient | Only shown if "Color mode" is set to "Gradient". Specifies gradient color values for mono16 and 16UC1 images. |
| Value min | Minimum scaling value for mono16 and 16UC1 depth images (default: 0). |
| Value max | Maximum scaling value for mono16 and 16UC1 depth images (default: 10000). |
Scene
| field | description |
|---|---|
| Render stats | Display rendering performance statistics in panel corner |
| Background | Color of background behind the image |
| Label scale | Size of text labels |
Ignore COLLADA <up_axis> | Ignore the <up_axis> tag in COLLADA files |
| Mesh up axis | Direction of “up” when loading meshes (STL, OBJ) without orientation info ("Y-up", "Z-up") |
Image annotations
2D image annotation marker topics to display.
Transforms
List of transform messages to display.
See the 3D panel docs for more information on possible settings.
Topics
List of 3D marker topics to superimpose on the image.
Custom layers
See the 3D panel docs for more information on possible settings.
User interactions
Right-click on the image to download it as a PNG file.

Click any displayed image marker to view its details.
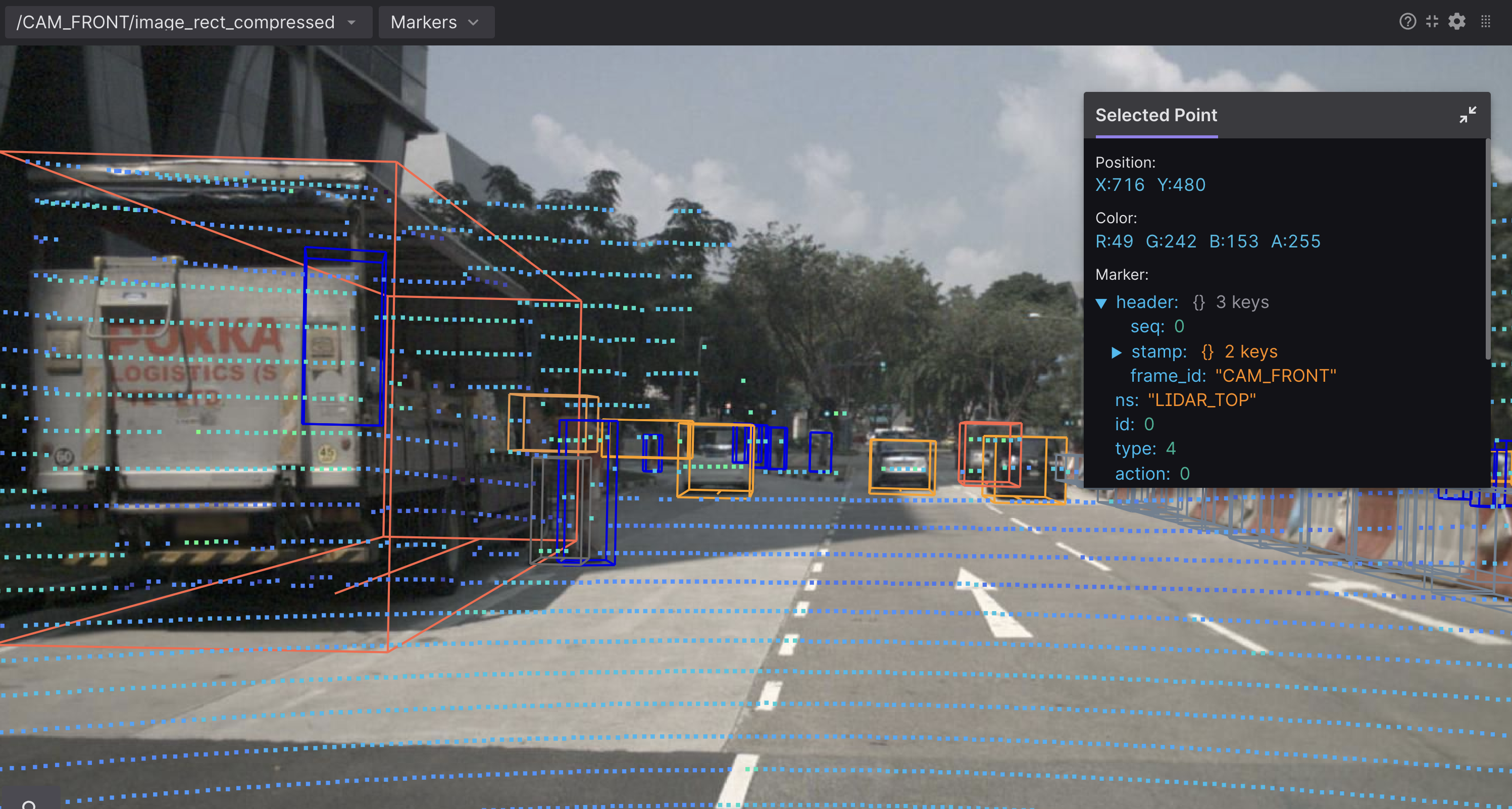
Scroll to zoom, and drag to pan. Annotations will re-render on zoom to remain sharp.
Shortcuts
- Scroll – Zoom in and out
Troubleshooting video delay
You may see errors for foxglove.CompressedVideo topics stating that the frame being displayed is delayed relative to the most recent frame. If the number of frames delayed is less than 10 and doesn't seem to grow after pausing, then this could be due to the video decoder on your platform. Video decoding behavior can vary across platforms, and some platforms may experience delays while others do not. It is possible to configure your video stream to optimize for low-latency decoding, but it may be impossible to guarantee that a video stream can be decoded with zero latency on all platforms.
Some tips on how configure the video encoding to best achieve low-latency decoding:
- Use the
BASELINEprofile forh264encoded streams. This profile is preferred because it does not support B frames. Profiles which support B frames may introduce decoding delay, even if the encoded stream doesn't actually contain B frames. - Disable frame reordering on your encoder.
- Lower profile levels (
level_idc) usually require smaller buffers, resulting in lower-latency decoding. - If your encoder allows it, use a
bitstream_restrictionin the VUI parameters to limit the size of the buffer (max_dec_frame_buffering) and also disable frame reordering (max_num_reorder_frames).
If you see that the frame delay increases after pausing that likely means that the video decoder can't keep up with your stream, and you'll want to reduce the number of your panels displaying video streams and/or check that your platform supports video acceleration. Read on to see more information.
System CPU load and power consumption may also contribute to decoding delays. Hardware-accelerated decoding is generally faster and more energy-efficient. Make sure to check that it is enabled.
These steps can help your platform achieve low-latency decoding, but there is no guarantee depending on the platform and device being used.
Checking video acceleration
You can check whether your platform supports hardware-accelerated video decoding by opening Google Chrome and entering chrome://gpu in the address bar. If you do not see Video Decode: Hardware accelerated or the Video Acceleration section is empty on this page, but you believe that it should be supported, then you may need to take additional platform-specific steps to enable it.
The desktop app uses Electron (based on Chromium), and should automatically use hardware acceleration when available. If you're seeing issues here, we recommend following the steps above to see if the same issue exists in Chrome. If so, there's a good chance it's affecting our application for the same reasons. We recommend getting things working in Chrome first, and if the desktop app is still having issues afterward please let us know and we'll look into it.
Enabling video acceleration
Tips for Flora web in Chromium browsers:
- Go to
chrome://settings, search your settings foraccelerationand ensure that the "Use graphics acceleration when available" toggle is enabled. - Go to
chrome://flags, search forvideoand ensure that "Hardware-accelerated video decode" is enabled.
MacOS:
- For web, significant performance gains have been observed when changing the graphics backend to use "Metal" in Chromium-based browsers. You can do this in
about://flags.
On Linux:
- Note that Chrome/Chromium doesn't support video acceleration on Linux by default and custom Chrome/Chromium flags may need to be used to enable it with your GPU.
- Ensure that your graphics drivers are up-to-date and installed properly.
